Term"diabetes mellitus"name the entire group of endocrine diseases, united by a common feature: they are based on carbohydrate metabolism disorders. In the body, there is a lack of the hormone insulin produced by the pancreas, or body cells stop responding adequately to it, which causes an increase in the level of glucose in the blood plasma. At the same time, the cells suffer from a lack of energy and starve, even with a sufficient amount of carbohydrates from food.
Among all endocrine diseases, diabetes mellitus in women and men is the most common. There are more than 250 million people in the world with different types of this pathology. In our country, diabetics make up about 6% of the total population. In some people, carbohydrate metabolism disorder and diabetes simply haven't been identified yet, so the actual percentage may be almost twice as high.
Causes of diabetes
Today there is no consensus on why this disease occurs. Today it is considered polyetiological - there are several theories about the origin of carbohydrate metabolism disorders and insulin problems. Unfavorable heredity plays a special role if close relatives suffer from diabetes.
In addition, certain factors and triggers can become provocateurs. this:
- poor diet with an excess of light carbohydrates, refined food, fast food, saturated and trans fats, and a lack of dietary fiber;
- overweight and obesity (BMI above 30 and fat deposits in the front abdominal wall are particularly dangerous);
- chronic disorders of water and electrolyte balance;
- endocrine pathologies (Cushing's disease, hyperfunction of the thyroid gland);
- long-term, chronic physical and psycho-emotional stress;
- complications of "childhood infections", especially measles, rubella and chicken pox;
- abdominal injuries affecting the pancreas;
- chronic inflammatory processes and organ pathologies - cysts, calcifications, pancreatitis, sclerosis, stones in the ducts.
A high risk of diabetes is possible in children born to mothers who suffered from the gestational form of the disease, if the baby was born with a high weight, had problems with glucose levels in the first days of life.
Symptoms of the disease
In the initial stage, diabetes mellitus practically has no pronounced symptoms. Often the first alarm bells are mistaken for overwork, infections or the effects of stress. However, it is important to pay attention to the combination of symptoms, which by themselves can be signs of other diseases, but in combination indicate the manifestation of diabetes.
The main signs of diabetes are:
- constant dry mouth, strong thirst with sufficient or excessive fluid intake;
- frequent urination, abundant urine output (up to 3-5 liters or more);
- dry skin, itching in the area of feet, elbows, legs;
- rapid weight gain or sudden weight loss;
- constant hunger despite proper nutrition;
- increased sweating, specific sweet smell of sweat and breath;
- slow healing of scratches and skin wounds;
- constant fatigue, drowsiness, reduced performance.
In addition, there may befainting, loss of consciousness, weakness, dizziness. Often, people first learn of their diagnosis when they are admitted to the hospital in a hyperglycemic or ketoacidotic coma.
Types of diabetes
There are two main forms of the disease, which have different causes and mechanisms of development, and in the initial phase, they differ significantly in treatment tactics.
Type 1 or insulin-dependent diabetes. It occurs as a result of an attack by the immune system on the cells of the pancreas that synthesize insulin. As a result, hormone production gradually decreases, reaching a critical level, while the level of glycemia (glucose in the plasma) increases. This form of diabetes occurs more often in children and young people at an older age, it is possible on the background of pancreatic necrosis due to complicated pancreatitis or organ removal. The basis of therapy is the administration of insulin.
Type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance (independent)it occurs more often in older people or people who are overweight. It is caused by impaired sensitivity of cells to insulin, which often occurs due to obesity and metabolic disorders. Correction is possible with diet and glucose-lowering drugs.
In addition, there are other specific forms of diabetes:
- gestational- occurs during pregnancy and is associated with metabolic disorders;
- pancreatogen- associated with injuries, severe damage to the pancreas;
- LADA-diabetes(short for latent autoimmune diabetes), has mild symptoms, does not require insulin injections;
- MODY-diabetes- This is a special, genetic form of the disease.
Any form of diabetes can have
Complications of the disease
If a patient with diabetes mellitus ignores the doctor's recommendations, does not follow a diet or refuses to take medication, the disease can be complicated by serious pathologies and changes in the body that threaten disability and even life. this:
- severe visual impairment, damage to the structures inside the eyeball and its vessels;
- formation of permanent hypertension (high blood pressure);
- disorders of lipid metabolism, increase of "bad" cholesterol, which leads to atherosclerosis;
- severe swelling of limbs;
- frequent headaches that reduce performance;
- sensory disorders in the extremities (neuropathy), blood flow disorders (angiopathy).
Against the background of metabolic disorders, life-threatening conditions can appear -
- Hypoglycemic comaIt is dangerous because it develops quite quickly and can lead to serious consequences. It occurs when the glucose level drops to less than 2. 8 mmol/l. Doctors can help with this by administering glucose doses with individually selected insulin levels.
- Ketoacidotic comaoccurs when glucose metabolism is disturbed when it increases in the blood. It breaks down into ketone bodies, which poison the body.
- Lactate comait occurs when there are malfunctions in glucose metabolism, due to which acidic metabolic products accumulate, which leads to respiratory and circulatory disorders and requires treatment in intensive care.
Diagnostics
Basic laboratory tests that confirm diabetes:
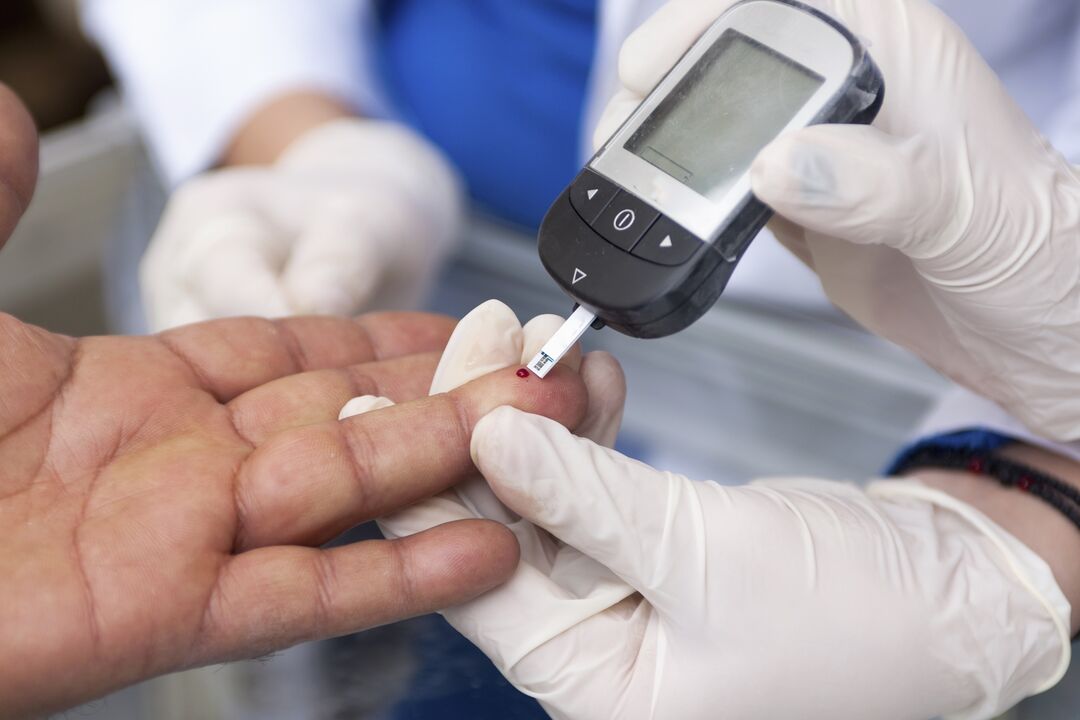
- blood test for glucose level (given in the morning, on an empty stomach);
- exercise test (determination of glucose tolerance (blood is taken on an empty stomach, then 1 and 2 hours after taking a glucose solution);
- biochemical studies (protein, lipid, electrolyte levels);
- evaluation of the level of glycosylated hemoglobin HbA1c;
- general and daily urine analysis with determination of glucose and protein levels;
- determination of endogenous insulin levels.
The doctor also prescribes a series of instrumental tests and consultations - an ophthalmologist's examination with an evaluation of the fundus, a neurologist's consultation with an assessment of the condition of the peripheral nerves, monitoring of blood pressure, EKG and ultrasound of internal organs and blood vessels.
Treatment
The basis of treatment is a combination of non-medical approaches, lifestyle changes with individual selection of drugs that control the level of glycemia in diabetes mellitus (fasting and post-meal blood glucose, activity). Treatment approaches differ depending on the type of disease.
For type 1 diabetesthe basis of drug treatment isinsulin injections(short, extended and other types depending on the severity of the condition and situation).With another speciesThe basis of glucose treatment and control isdiabetes tablets. They help to reduce glucose levels while adjusting the diet. It is important to emphasize that the treatment is carried out for life, with dose adjustment and dynamic monitoring of the patient.
In controlling diabetes, it is important to follow a diet that provides the body with all the necessary nutrients, vitamins and minerals, but does not cause sudden spikes in blood sugar. The doctor helps in correcting the diet, teaches the patient how to choose the right foods and their combination with medication or insulin. All products for diabetes are divided into groups - those that can be used without fear, those that should be reduced and those that should be excluded.
In addition, the doctor recommends changes in lifestyle - weight control, physical activity, regular visits to the doctor to prevent complications of the pathology.
Prevention
In order to maintain health and reduce the risk of developing diseases, it is necessary to control your weight, regularly evaluate carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, and undergo medical examinations. Moderate physical activity, sufficient fluid intake and a balanced diet with a reduction in carbohydrates, saturated fat, fast food and refined food are important.